The Difference Between Primary and Secondary Growth Biology - Growth and development in plants always take place simultaneously. In both processes there are events such as cell division, increased cell size, and cell maturation (differentiation). Well, in our article today i will discuss about The Difference Between Primary and Secondary Growth Biology. Are you curious? So, let's continue reading this article
Primary Growth
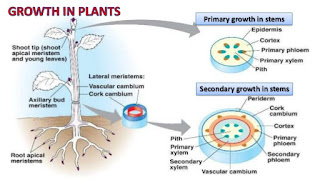 |
| Primary Growth vs Secondary Growth |
Growth in plants occurs due to the activity of meristem cells. Meristem cells are cells that actively divide by mitosis. Many meristem cells are found at the root until root ends of stems or buds. Such a meristem is called an apical meristem. Apical meristem cells often divide throughout plant life. Apical meristem activity causes the roots and stems to grow longer. The process of division of meristem cells that cause plants to grow length is called primary growth. Primary growth allows roots to penetrate through the soil layer and shoots or levers grow upward, so that they get a lot of light and carbon dioxide.
A. Primary Growth in Roots
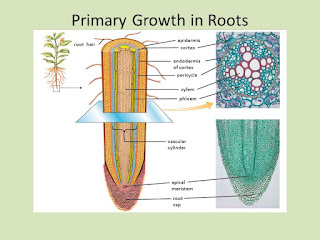 |
| Primary Growth in Roots |
The activity of meristem cells in roots allows roots to grow into deeper layers of soil. At the tip of the root there is a root cap (caliptra) that serves to protect the root when it penetrates the soil layer. Roots can be divided into three zones, namely cleavage zones, elongation zones, and maturation zones.
The cleavage zone includes the apical meristem region of the root and its derifat cells. In this zone, cells divide rapidly to produce new cells and the formation of a root cap. The elongation zone includes the elongation area of cells whose length can extend more than 10x the length of ordinary cells. Maturation zone, there area three tissue systems of mature plants, namely dermal tissue, basic tissue, and vascular tissue.
Dermal tissue (epidermis) is formed by protoderm. Protoderm is the outermost layer of the meristem. The basic tissue is the innermost layer of the apical meristem. While the vascular tissue (vessel cylinder) is a carrier tissue consisting of primary xylem and primary phloem. This tissue is formed by procambium which is located between protoderm and the basic meristem tissue.
B. Primary Growth on the Stem
There are two types of shoots in plants, namely terminal shoots and axillary shoots. The terminal shoots are flanked by ovaries (primordia) and are located at the tips of the stems that allows plants to grow upward. Axillary shoots (lateral buds) are located on the armpits of the leaves whose growth will form branches or flowers.
Secondary Growth
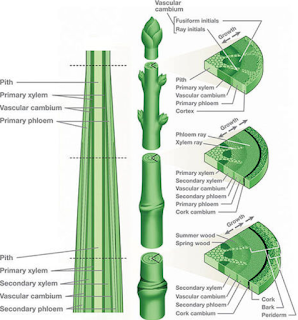 |
| Secondary Growth |
Plants, in addition to growing elongated can also grow bigger. Growth that allows an increase in the diameter of the stem and roots is called secondary growth. All gymnosperms and dicots develop secondary growth. However, this secondary growth does not occur in monocotyledonous (monocots) plants. Secondary growth occurs only certain monocotyledonous plants, such as Palmae.
Secondary growth occurs due to the activity of lateral meristem cells. There are two types of lateral meristem, namely vascular cambium and cork cambium. The vascular cambium is located between the xylem and phloem. Vascular cambium activity produces new cells. These new cells are in the form of secondary xylem (inward) and secondary phloem (outward).
On the trunk, the xylem which we know as wood, the layer more longer, thicker and ligneous. This makes the wood hard. The xylem tissue that forms during the dry season usually has smaller, and darker cells. This is caused by limited water supply during the dry season. Conversely, xylem tissue formed during the rainy season has cells that are relatively large and lighter in color. The layers formed from the formation of wood tissue are often known as the circle of the year.
Okay everyone. That is our article today which deals with The Difference Between Primary and Secondary Growth Biology. I hope this article can be useful for all of you. Good bye and see you later ^^



Thank you for reading. Don't forget to read other interesting articles ^^
ReplyDeleteNice, thank you. Now i can more understand about it
ReplyDelete